What is Kubernetes and How to Use it on AWS

What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes is an open-source platform designed to automate deploying, scaling, and operating application containers. It is developed by Google and is now maintained by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). Kubernetes can be used to manage and orchestrate containerized applications, regardless of where they run.
Kubernetes is a powerful tool for deploying and managing containerized applications in a production environment. It provides a highly scalable, highly available infrastructure that can automatically manage containerized workloads across a cluster of nodes.
How does Kubernetes work?
At its core, Kubernetes is designed to manage containerized workloads across a cluster of nodes. It does this by providing a highly available and highly scalable infrastructure for running containerized applications.
Kubernetes uses a declarative configuration model, which means that you define the desired state of your application, and Kubernetes will take care of the details of making sure that the actual state of your application matches the desired state.
Kubernetes also provides a rich set of APIs for managing containerized workloads. You can use these APIs to create and manage Kubernetes resources, such as pods, services, and deployments.
Kubernetes Architecture
Kubernetes is built around a master-worker architecture. The master node is responsible for managing the cluster, while the worker nodes are responsible for running the containers.
The master node consists of several components, including the Kubernetes API server, the etcd data store, the Kubernetes scheduler, and the Kubernetes controller manager.
The Kubernetes API server is the main management point for the cluster. It provides a RESTful API that can be used to create and manage Kubernetes resources.
The etcd data store is a distributed key-value store that is used to store all of the state information for the cluster. It provides a highly available and highly scalable data store that can be used to store all of the configuration and state information for the cluster.
The Kubernetes scheduler is responsible for scheduling containerized workloads across the cluster. It takes into account the resource requirements of each workload and the available resources on each node to determine the optimal placement of each workload.
The Kubernetes controller manager is responsible for managing the various controllers that are used to manage the state of the cluster. It includes controllers for managing pods, services, deployments, and more.
The worker nodes are responsible for running the containers. Each worker node runs a Kubernetes agent called the kubelet, which is responsible for managing the containers on that node. Each worker node also runs a container runtime, such as Docker, which is used to run the containers.
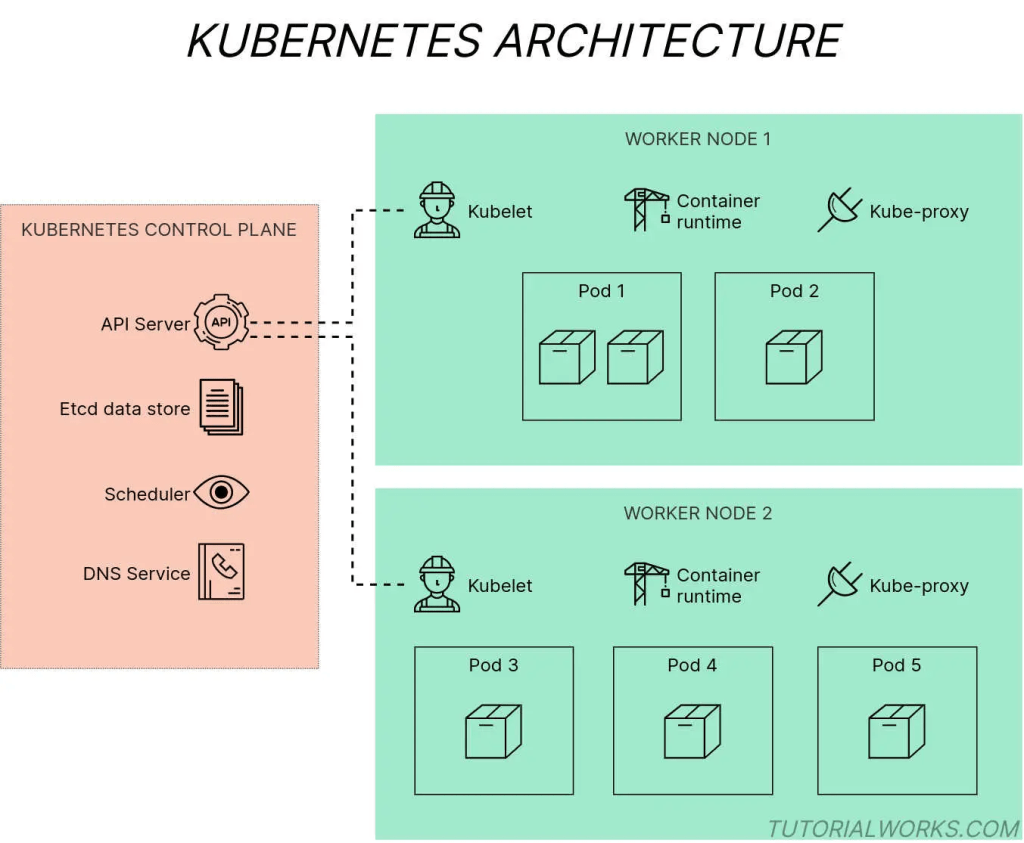
Kubernetes architecture diagram by Tom Donohue is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
Kubernetes Resources
Kubernetes provides a rich set of resources for managing containerized workloads. These resources include:
- Pods: Pods are the smallest deployable units in Kubernetes. They are used to run one or more containers together on the same host.
- Services: Services are used to provide a stable network endpoint for accessing pods. They can be used to load balance traffic across multiple pods and to provide a single DNS name for accessing a set of pods.
- Deployments: Deployments are used to manage the deployment of pods. They provide a declarative way to manage the desired state of the pods and to perform rolling updates and rollbacks.
- ConfigMaps: ConfigMaps are used to manage configuration data for your application. They can be used to store environment variables, configuration files, and more.
- Secrets: Secrets are used to manage sensitive data for your application. They can be used to store passwords, API keys, and more.
Using Kubernetes on AWS
AWS provides a number of services that can be used to run Kubernetes workloads. These services include Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) and Amazon Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes (ECS-Kubernetes)

Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) is a fully managed Kubernetes service that makes it easy to run Kubernetes on AWS. With EKS, you don’t need to worry about managing the master nodes, as AWS takes care of this for you. You only need to manage the worker nodes, which can be launched using Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) instances or AWS Fargate.
To get started with EKS, you first need to create a Kubernetes cluster using the EKS console, CLI, or API. Once you have created the cluster, you can launch worker nodes using EC2 instances or AWS Fargate. EKS provides an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) that includes the Kubernetes agent and the necessary tools for managing the worker nodes.
After launching the worker nodes, you can deploy your containerized applications to the cluster using Kubernetes resources, such as pods, services, and deployments. EKS integrates with other AWS services, such as Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) and AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), to provide a seamless experience for managing your Kubernetes workloads on AWS.
Amazon Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes (ECS-Kubernetes)
Amazon Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes (ECS-Kubernetes) is another service provided by AWS for running Kubernetes workloads on AWS. ECS-Kubernetes is built on top of Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS), which is a fully managed container orchestration service provided by AWS.
With ECS-Kubernetes, you can deploy and manage Kubernetes workloads using familiar Kubernetes APIs and tools. ECS-Kubernetes runs the Kubernetes control plane as a managed service, so you don’t need to worry about managing the master nodes. You only need to manage the worker nodes, which can be launched using EC2 instances or AWS Fargate.
To get started with ECS-Kubernetes, you first need to create a Kubernetes cluster using the ECS-Kubernetes console, CLI, or API. Once you have created the cluster, you can launch worker nodes using EC2 instances or AWS Fargate. ECS-Kubernetes provides an AMI that includes the Kubernetes agent and the necessary tools for managing the worker nodes.
After launching the worker nodes, you can deploy your containerized applications to the cluster using Kubernetes resources, such as pods, services, and deployments. ECS-Kubernetes integrates with other AWS services, such as Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) and AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), to provide a seamless experience for managing your Kubernetes workloads on AWS.
Conclusion
Kubernetes is a powerful platform for deploying and managing containerized applications in a production environment. It provides a highly scalable, highly available infrastructure that can automatically manage containerized workloads across a cluster of nodes.
AWS provides several services for running Kubernetes workloads on AWS, including Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) and Amazon Elastic Container Service for Kubernetes (ECS-Kubernetes). These services make it easy to get started with Kubernetes on AWS and provide a seamless experience for managing your Kubernetes workloads.
